Kalshi vs. Polymarket: Complete Comparison & Review (2026)
We believe in full transparency with our readers. Some of our content includes affiliate links, and we may earn a commission through these partnerships. However, this potential compensation never influences our analysis, opinions, or reviews. Our editorial content is created independently of our marketing partnerships, and our ratings are based solely on our established evaluation criteria. Read More
A key reason why prediction markets are becoming more popular is that they turn actual future events into “tradable contracts.” For example, you can simply buy and sell “Yes/No” shares that usually trade between $0 and $1, where the current price acts like the crowd’s implied probability.
Retail interest in these contracts has massively grown as the category has moved closer to mainstream finance. Kalshi and Polymarket are currently the leading names in the prediction market segment. Even though both have faced legal challenges related to their operations, they’ve almost formed a duopoly, capturing the bulk of trading volumes.
For perspective, Kalshi won a court case back in 2024 that cleared the way for it to list US election contracts. And in the meantime, Polymarket has rebuilt itself into a two-track business: an offshore crypto platform plus a regulated US lane (Polymarket US) recognized by the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC).
Our detailed Kalshi vs. Polymarket comparison will help you understand their legal standing and fee structures, among other key factors. Read on to see how they stack up and which platform is ideal for your trading style.
Overview: Which Is Better – Kalshi or Polymarket?
- Our research shows that Kalshi is better for users who prefer a federally regulated platform that allows direct USD deposits.
- And Polymarket is ideal for crypto enthusiasts who are more comfortable with stablecoin (mainly USDC) settlement. It also offers a vast selection of markets across various sectors and often charges ultra-low platform trading fees.
To provide more context, Kalshi’s onboarding process is quite similar to that of traditional finance (TradFi) platforms. It requires identity verification to comply with U.S. laws and CFTC rules, and its fee schedule clearly outlines ACH, debit, wire, and crypto funding costs in simple terms. That clarity and the ability to deposit from a bank account basically reduce the initial friction that beginners typically face.
On the other hand, Polymarket may feel like a crypto exchange that happens to trade events. Users will need to mainly fund their accounts in USDC, trade, and then withdraw their earnings in USDC as well. But Polymarket has an edge in fees, as its global platform charges near-zero fees, which is highly desirable for frequent traders. Thus, it can be ideal for you if you’re already comfortable with stablecoins.
While both are among the best prediction market platforms in 2026, Kalshi’s trading fees are tightly tied to the contract price, whereas Polymarket has historically been fee-free on most markets, but has added taker fees on specific crypto markets.
| Quick Takeaway | Kalshi | Polymarket |
| Best Fit | U.S. retail traders who prefer regulation and direct USD deposits. | Web3 users who prefer stablecoin settlements and near-zero fees. |
| Strength | Regulated by CFTC with exchange-style rules. | Doesn’t charge a fee for trading on most markets. |
| Watch Out For | Low liquidity outside major contracts, causing wider spreads and harder entry or exit. | Regulatory rules vary by jurisdiction, creating uncertainty, and sudden market restrictions. |
What Are Kalshi and Polymarket?
From a big-picture perspective, both Kalshi and Polymarket operate as “event derivatives” exchanges. Unlike a sports bookmaker, where you bet against the house, these are exchanges with a Central Limit Order Book (CLOB).
When you buy a “Yes” contract, you are trading against another user selling that “Yes.” Kalshi and Polymarket both use binary event contracts that are priced as probabilities.
For example, a contract at 65 cents means the market thinks there’s a 65% chance the event happens. If you buy at $0.65 and the event actually happens, you’ll receive $1, earning a $0.35 profit. If it doesn’t, you will lose your principal.
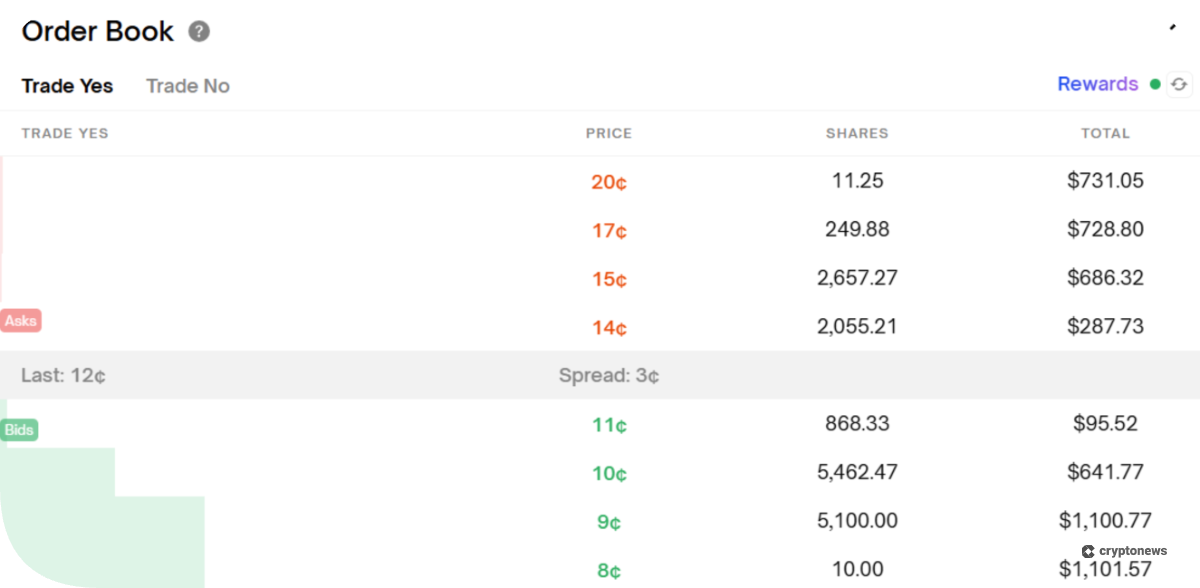
The fundamental difference between them lies in their operating models and legal standing. To begin with, Kalshi is a centralized platform that is running on private servers. It segregates funds in US bank accounts and also reports every transaction to the CFTC.
Polymarket, however, is a dApp that is built on the Polygon blockchain. It’s decentralized, meaning no central authority holds your funds, so you will have to control your wallet directly. The model resonates well with tech-savvy users, but it faced US bans until a 2025 relaunch.
While Polymarket’s main protocol is regulated offshore, it has built a US version that complies with the CFTC rules. It is worth noting that these rules require the platform to offer its services through an intermediary exchange.
Are Kalshi and Polymarket the Same Company?
No. Kalshi and Polymarket are separate companies with different leadership and strategies. In fact, Kalshi is a popular alternative to Polymarket for U.S. users seeking higher regulatory clarity.
Kalshi was founded in 2018 by MIT grads Tarek Mansour (CEO) and Luana Lopes Lara (COO). It is privately owned and backed by top VC companies like Sequoia Capital, Paradigm, and Charles Schwab. Kalshi even raised a Series E round in late 2025, valuing the company at about $11 billion.
On the other hand, Shane Coplan founded Polymarket in 2020 after receiving backing from Peter Thiel’s Founders Fund, Vitalik Buterin, as well as Intercontinental Exchange (ICE).
Polymarket Vs. Kalshi Comparison
Here are some of the key factors to consider when choosing the right platform for your trading style.
Regulation & Legality
Kalshi is a fully regulated US exchange that is registered with the CFTC as a Designated Contract Market (DCM). It has the same legal status as any other American futures exchange, such as ICE.
Over the years, Kalshi has been involved in multiple legal battles. For instance, the CFTC initially restricted Kalashi’s political markets, but it fought back in court. It eventually won a Summary Judgment, effectively receiving the green light to operate prediction markets in sensitive categories like elections.

Even so, many US state regulators have already issued cease-and-desist orders, claiming that Kalshi’s sports contracts violate state gambling laws. And in a remarkable move, a Massachusetts Superior Court judge ruled on January 20 that Kalshi needs a license to offer sports-event contracts to Massachusetts residents. Kalshi’s stance remains that its federal approval preempts state laws, and plans to appeal this decision.
Unlike Kalshi, Polymarket started out without a US regulatory approval. It operated in a legal gray zone in 2020-21, which eventually drew the CFTC’s attention. In early 2022, the CFTC fined Polymarket $1.4 million for running an unregistered exchange, and Polymarket agreed to block US users shortly thereafter.
To comply with regulations, Polymarket has acquired a CFTC-regulated exchange, creating a regulated pathway for operating in America. Polymarket US is currently in a limited rollout; it has been tested with select users and is available via a waitlist.
👉 Learn More: Is Polymarket Legal in the US?
Market Size, Volume & Liquidity
Polymarket was widely seen as the category leader for a long stretch, but Kalshi overtook it on volume in late 2025. In 2025, Kalshi recorded about $27.3 billion in notional trading volume, compared with $24.1 billion on Polymarket. For context, Kalshi currently claims more than 60% of the market share.
It is also worth knowing that a recent study from Columbia University flagged signs of wash trading on Polymarket’s global platform, suggesting that some trading volume may have been artificially inflated.
From a liquidity perspective, Kalshi runs like a traditional order-book exchange supported by market makers. Similarly, Polymarket uses an order book, where market makers post bids and asks. The only difference is that Polymarket matches the trades and settles them on-chain on Polygon.
Fees & Costs Breakdown
These platforms follow very different fee structures. Here’s a detailed table that breaks down and compares Polymarket’s main costs and fees versus Kalshi:
| Cost Type | Kalshi | Polymarket (Global) | Polymarket US (Beta) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trading fee | It is variable, formula-based. Taker fees apply when your order matches immediately, and some markets may also have maker fees. Formula: 0.07 × C × P × (1–P), rounded up.
C – Contracts |
0% on most markets. On 15-minute crypto markets, the taker fee varies by price, with a maximum effective fee of 1.56%. | Taker fee: 0.10% (10 bps) of total contract premium. |
| Deposit fee | ACH: $0.
Debit: 2%. Crypto: may include third-party processor fees that will be disclosed before you confirm. |
No platform fee for depositing or withdrawing USDC. Although Coinbase/MoonPay or other intermediaries may charge a fee.
Polygon network fees may also apply. |
Broker dependent. |
| Withdrawal fee | ACH: $0.
Debit: $2. Wire: only supported for very large withdrawals of $500,000 or more. Crypto: may include third-party processor fees. |
No platform withdrawal fee. Users should still watch out for network gas fees. | Broker dependent. |
| Interest on cash | Yes (Kalshi Klear): 3.25% APY on holdings. | No interest in idle cash. Instead, there’s currently a 4% holding reward on eligible positions in certain markets. | None |
Here is a simple cost comparison for:
- Casual traders: Kalshi can be cheaper if you’re starting in USD because ACH deposits as well as withdrawals are $0 on top of Kalshi’s per-trade fees. Polymarket can be cheaper if you already have USDC, as it charges no trading fees on most markets and no platform fees for depositing or withdrawing USDC.
- High-frequency traders: Kalshi’s transaction fees can stack up quickly at high turnover. They typically scale with contract price and size and are highest around mid-priced contracts. Polymarket is usually lower-cost for HFT because most markets don’t charge fees, except for the 15-minute crypto markets. If you’re looking at Polymarket US specifically, it charges a 10 bps taker fee on total contract premium, which can still add up with HFT.
Funding, Currency, and User Experience
Kalshi mainly accepts USD, but it also supports crypto transfers via third-party providers. On the other hand, Polymarket mainly uses USDC on Polygon for balances and settlement. We found that the overall user experience is fundamentally different on both platforms. On Kalshi, you can open a new account only after completing identity checks, while linking a bank account for ACH. Since it’s regulated by the CFTC, customer funds are held in a segregated US bank account dedicated to them.
On Polymarket, you must first connect a wallet and then use USDC. Any identity checks typically come from third-party onramps rather than a brokerage-style KYC step in the core flow. Polymarket’s CLOB authentication is built around private-key signing and runs on Polygon for transactions and settlement.
👉 Learn More: Best Polymarket Wallets for Secure Trading in 2026
When deciding which platform is right for you, you can choose Kalshi if you want regulated USD banking options without managing a Web3 wallet. Alternatively, you can instead use Polymarket if you’re comfortable with wallets and are outside restricted regions.
Arbitrage Opportunities
Even if two contracts are about the same event, their prices can still differ across Kalshi and Polymarket. That is typically due to liquidity and, more importantly, the specs of each contract. Both Polymarket and Kalshi define the “Yes/No” outcome differently, meaning there are different terms on what exactly counts as a win and when the result is considered final.
Having said this, it is important to know that arbitrage is relatively harder than it looks because of these reasons:
- Geo-Restrictions: Polymarket has historically blocked American residents following the CFTC settlement, while Kalshi is a CFTC-regulated exchange. In fact, Kalshi is still facing state-level battles over certain products like sports contracts. It significantly reduces arbitrage opportunities for traders who can’t legally place trades on both platforms.
- Capital Transfer: Moving capital between platforms isn’t instant. Polymarket collateral is USDC.e, where deposits are often bridged into the trading collateral. Whereas Kalshi supports multiple funding methods, and even its own help docs note that transfer options vary for international users. As a result, bank delays and exchange withdrawal limits create a window where the spread can vanish.
- Resolution Timing: Kalshi states that most markets settle within a few hours after the outcome is known, but it can take longer when official confirmation is delayed. Conversely, Polymarket resolutions run through an “Optimistic Oracle process,” where outcomes can be proposed and disputed before finalization. That timing mismatch can trap capital on one side while the other leg is still pending.
Market Types and Event Variety
We found that Kalshi’s market catalog leans heavily toward “measurable” topics like macro releases, including inflation rates, Fed interest rate decisions, and unemployment numbers. It also includes political events, climate and weather events, and a lot of sports/entertainment contracts.
Kalshi currently offers around 3,500 markets, but most fall within a curated set of categories, where the outcomes are generally easier to define and source. The small number of markets and slower pace are among the main reasons why users search for Kalshi alternatives.
Polymarket, on the other hand, allows markets for almost anything that users propose within reason. You’ll see plenty of politics and finance, as well as Web3 events, tech, pop culture, and even bizarre internet memes.
To put this in perspective, Polymarket has hosted markets on celebrity news, viral internet memes, and crypto culture, alongside serious topics like elections and recession odds.
Safety, Reputation, and Trust
To begin with, Kalshi runs under US regulatory oversight, which gives it a stronger credibility floor. As we discussed, the platform will segregate customer funds and follow standard compliance rules, including audits and ongoing checks.
Perhaps the biggest draw of this regulated approach is that if something goes wrong, users have a formal path to raise issues through the CFTC.
Another important factor is that Kalshi has had no known major security breaches to date. It even goes a step further, offering responsible trading features such as deposit limits and self-exclusion to help users stay in control. For these reasons, Kalshi is legitimate and safe.
By comparison, Polymarket’s path has been bumpier. In its early days, it was mainly operating in a gray regulatory area and relied on its tech and user base to build trust. From a tech perspective, trades run through smart contracts, and outcomes are settled using UMA’s Optimistic Oracle on-chain. The system has already handled hundreds of markets without major issues, which shows relatively high resilience.
Another big advantage is that no single company can easily steal users’ funds or manipulate results because Polymarket is a decentralized prediction market. The flip side of operating outside strict regulation is that protections are lighter, so if something went wrong, users have fewer recourse options.
Our research shows that Polymarket is safe since it hasn’t experienced any major smart contract hacks to date. Since it’s wallet-based, users hold their own funds rather than the platform holding them in custody.
- Largest decentralized prediction market platform
- Zero trading fees across most markets
- Highest trading volume and liquidity
How Prediction Markets Work
A prediction market contract is basically a $1-or-$0 claim on a specific outcome. Each market has a question, a resolution window (when it will be decided), and rules that define exactly what counts as “Yes” and where the final answer comes from.
If a “Yes” share trades at $0.65, traders are paying $0.65 for a claim that will be worth $1 if it occurs and $0 if it does not. Because the payoff is binary, the $0.65 price corresponds to a 65% probability in our example. A “No” share will be worth $0.35 in this binary setup.
Importantly, you don’t have to hold your share until the event resolves. If you buy “Yes” at $0.65 and later the market reprices “Yes” to $0.8, you can choose to sell and lock your profits.
But if you hold a “Yes” share through resolution:
- If the outcome is “Yes,” it settles at $1.
- If the outcome is “No,” it settles at $0.
In prediction markets, the headline or main question is often used to attract traders, whereas the real value lies in the rules. Two contracts can look identical but settle differently because of details like timing or data sources.
Before trading on any prediction market, it is important to know who or what event will determine the outcome. For instance, it could be an official government announcement or even a bank’s reference rate.
Traders should then pay close attention to the specific language of the rules to ensure they are on the same page as the platform. They should also ask questions like what happens if a game is delayed, if data is later corrected, or if there’s a disagreement over the outcome.
Responsible Trading and Risk Consideration
Event contracts tend to “gap” because a single piece of new information can instantly change what people think will happen. A single headline or data release can swing prices in just minutes. If you wait until settlement at either $1 or $0, there is no room for being partially correct.
There is also a risk that the displayed price may be misleading because of thin liquidity. A small order can move the price a lot, so the last traded number may reflect one person’s urgency instead of the crowd’s true belief.
Most traders don’t get wiped out because of their wrong guess; they get wiped out because they bet too big. This is precisely why discerning traders cap their losses per trade, avoid going all-in on outcomes, and use limit orders to prevent bad fills in thin markets. They also track fees and transfer costs, as they can quickly add up. We found that Kalshi offers tools like Trading Breaks and funding caps to help traders better manage prediction market risks.
Prediction markets can tempt people to trade using inside information. If you buy or sell based on material non-public information, like confidential company plans or unreleased government numbers, you could face legal trouble and damage your reputation.
The CFTC can also investigate trades that appear to be fraudulent or manipulative, including cases of misleading others or coordinating trades.
Final Verdict: Kalshi Vs Polymarket (2026 Outlook)
No matter which platform you choose, event markets typically carry a relatively high trading risk. Thus, it is important to read the contract rules carefully and only risk what you can afford to lose.
We recommend opting for Kalshi only if you are looking for a US-regulated platform that lets you easily deposit and withdraw USD. If those aren’t your main priorities, Polymarket is the best choice — and its regulated American platform, which is being rolled out, could make it an even better pick this year.
Click below to explore a wide variety of markets and crypto-based trading.
Visit PolymarketFaqs
Is Kalshi legal in the USA?
Is Polymarket legal in the USA?
Who is Polymarket’s main competitor?
Does Kalshi or Polymarket have more volume?
Is Kalshi fully regulated?
References
- Kalshi cannot operate sports-prediction market in Massachusetts, judge rules (Reuters)
- Polymarket Testing US Prediction Market in Move to Reopening (Bloomberg)
- 2025 Annual Crypto Industry Report (CoinGecko)
- Network-Based Detection of Wash Trading (SSRN)
- 17 CFR § 180.1 – Prohibition on the employment, or attempted employment, of manipulative and deceptive devices (Cornell Law School)
About Cryptonews
Our goal is to offer a comprehensive and objective perspective on the cryptocurrency market, enabling our readers to make informed decisions in this ever-changing landscape.
Our editorial team of more than 70 crypto professionals works to maintain the highest standards of journalism and ethics. We follow strict editorial guidelines to ensure the integrity and credibility of our content.
Whether you’re looking for breaking news, expert opinions, or market insights, Cryptonews has been your go-to destination for everything cryptocurrency since 2017.
















