Bitcoin Public Ledger: What It Is and How to View It
The Bitcoin public ledger is a transparent record of all Bitcoin transactions. You can view every transaction, but personal details stay hidden. It’s like a bank statement that everyone can see, but only you know your account details. This builds trust and prevents fraud by ensuring all transactions are verifiable.
Key Takeaways
- The Bitcoin public ledger is a decentralized system that keeps track of Bitcoin transactions.
- It uses cryptography and public and private keys to maintain security and privacy.
- The public ledgers provide a semi-anonymous process that keeps your identity private while the information about balances and transactions is public.
What Is the Bitcoin Public Ledger?
Bitcoin is a decentralized digital currency that lets you store and transfer value without banks or other intermediaries. Its underlying technology, blockchain, powers this system.
Blockchain technology is a distributed ledger that records all transactions across a network of computers. Each transaction is grouped into blocks and linked in chronological order through cryptographic hashes, which guarantees the network’s high security and transparency. In this context, a public ledger is an open and accessible record of all Bitcoin transactions. The Bitcoin public ledger is decentralized, meaning no single entity controls it, and everyone can view its data.
The ledger is transparent, as anyone can check any transaction, and immutable, ensuring that it cannot be altered. This decentralized database guarantees that the Bitcoin network remains secure and free from manipulation. This occurs because all participants help verify and maintain the ledger’s integrity.
Unlike traditional centralized ledgers, maintained by a single authority like a bank, Bitcoin’s public ledger is distributed across an extensive network of computers (nodes). Decentralization prevents any single point of failure, making the system more resilient to attacks or fraud. The public ledger is indispensable for ensuring the transparency and security of the Bitcoin network. This characteristic allows you to trust the system without needing to trust a central authority.
How Does the Bitcoin Blockchain Public Ledger Work?
The Bitcoin blockchain public ledger operates through a series of well-defined steps that ensure secure, transparent, and decentralized transaction processing. Each transaction is verified, bundled into blocks, and added to the blockchain, forming an immutable chain of data. This system leverages cryptographic techniques and consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work (PoW) to maintain the integrity and security of the network. Below is a breakdown of the key steps involved in the Bitcoin blockchain’s functionality:
Transaction Initiation
The Bitcoin blockchain public ledger begins with transaction initiation, where you digitally sign transactions using your private keys. After signing, the transaction is broadcast to the network, making it visible to all nodes. These nodes then confirm the transaction’s authenticity by verifying the digital signatures and ensuring the sender has sufficient funds.
Transaction Verification
The next step is transaction verification, where nodes and miners play vital roles. Nodes check the transaction’s validity, and miners then work to include it in a new block. Miners solve a complex mathematical puzzle using the Proof of Work (PoW) mechanism. The first miner to solve this puzzle bundles the verified transactions into a block and adds it to the blockchain. This is called block creation and mining, which helps secure the network and rewards miners with newly issued Bitcoin.
Block Creation and Blockchain Encryption
Once a block is created, it is added to the blockchain in linear, chronological order. Each block is cryptographically linked to the previous one using cryptographic hashes and blockchain encryption, creating an unbreakable chain. This structure ensures that any attempt to modify a block will change its hash, which alerts the network of tampering.
Consensus and Security
Consensus is achieved across the network using Proof of Work (PoW), ensuring that all participants agree on the blockchain’s validity. The use of cryptographic hashes guarantees data integrity, and any change in a block would be detected by the network. This decentralized system ensures that Bitcoin’s blockchain remains secure, transparent, and immutable.
Where Is the Bitcoin Public Ledger Stored?
One of blockchain’s key features is its distributed nature. Instead of being stored in a central database, the Bitcoin ledger is stored across thousands of blockchain nodes (computers) worldwide.
Full nodes and mining nodes maintain a complete copy of the blockchain, ensuring the system is decentralized and resistant to attacks or failures. This distribution makes it nearly impossible for any single entity to alter or corrupt the blockchain. They independently verify every transaction and block, ensuring the integrity of the network. By doing this, full nodes help uphold Bitcoin’s transparency and security.
However, scalability challenges arise as the Bitcoin blockchain grows with more transactions. The size of the blockchain increases, requiring more storage and bandwidth for nodes to keep up. Various solutions, such as Layer 1 and 2 technologies, are being explored to address blockchain scalability and make the network more efficient without compromising its security.
Who Can Access the Bitcoin Public Ledger?
Anyone with internet access can view the Bitcoin ledger, thanks to the public and transparent nature of blockchain technology. This means that all Bitcoin transactions are recorded on the blockchain and available for anyone to see, ensuring transparency in the system.
However, while the ledger is open, the wallet addresses involved in transactions are pseudo-anonymous. These addresses are not directly tied to personal identities, meaning you are represented by alphanumeric codes rather than your own name, providing a layer of privacy.
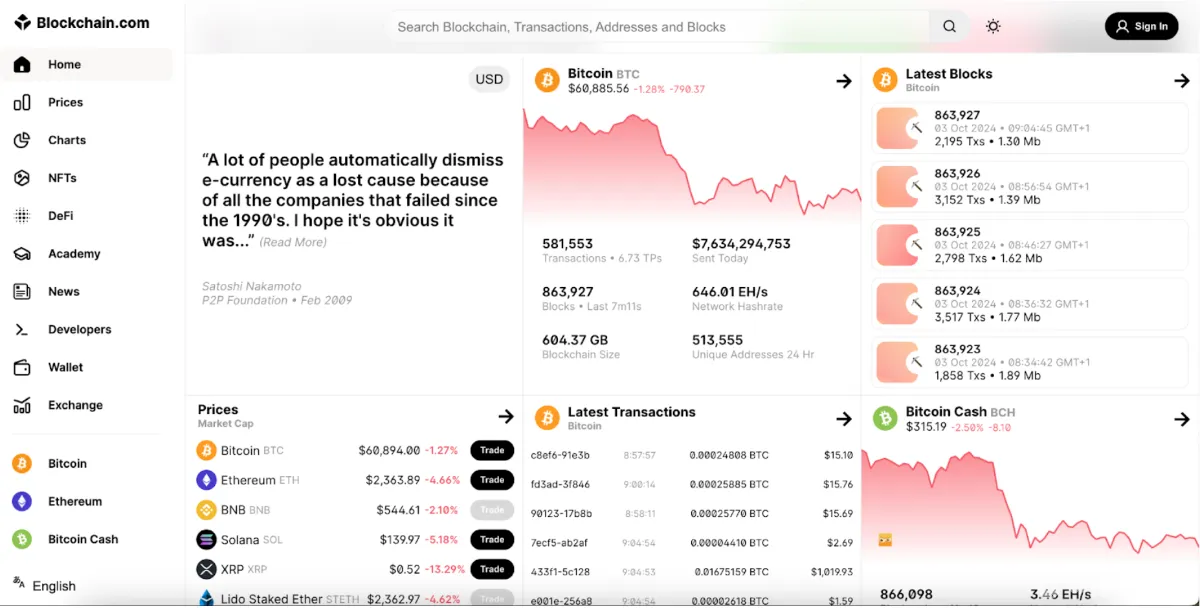
Block explorers are essential tools for examining the ledger. These web-based tools allow you to search the blockchain for transaction details, block histories, and wallet balances.
Blockchain explorers give you a closer look at what’s really going on with Bitcoin. By letting you download the whole blockchain, you can check transactions yourself instead of relying on others. There are quite a few ways to dig into the blockchain data and make sure everything checks out. This hands-on approach lets you feel confident about the information you’re seeing.
Bitcoin Ledger and Wallet Addresses
A wallet address is a unique identifier used to receive cryptocurrency like Bitcoin. It is generated from a pair of cryptographic keys: public and private keys. The public and private keys work together to guarantee secure transactions.
The public key generates your wallet address, which others can use to send you funds. You use the private key to sign transactions and verify ownership of the funds linked to your wallet.
Keeping your private key secure is fundamental, as it provides access to the funds associated with your Bitcoin wallet address. Someone who obtains your private key can control and spend your Bitcoin. You can share your public wallet address openly, as it poses no security concerns.
Block explorers can help you find your public wallet address in the ledger. You can enter your wallet address in the search bar to view its transaction history and balance.
How to View the Bitcoin Public Ledger?
A block explorer is a web-based tool that allows you to view and search blockchain data. It includes transaction histories, wallet balances, and specific blocks. It serves as a transparent window into the blockchain, providing anyone with access to real-time data from the network.
One popular example is the Blockchain.com explorer, which offers an easy-to-use interface for exploring the Bitcoin blockchain. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to use this explorer:
1. Visit the Blockchain Explorer: Navigate to [Blockchain.com Explorer] using your browser.

2. Search for a Transaction or Wallet: In the search bar at the top of the page, enter a Bitcoin wallet address, transaction ID (TXID), or block number, then click “Search.”
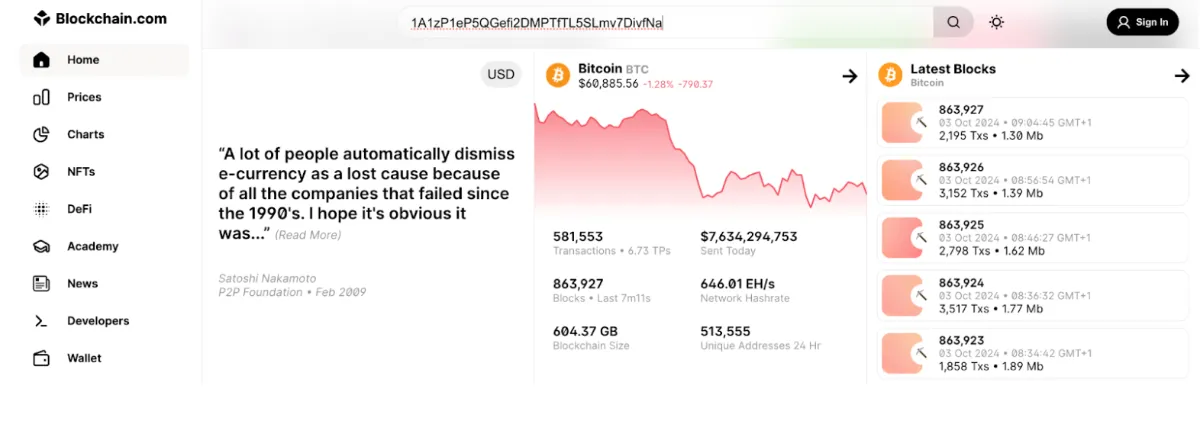
3. Check Wallet Balance: Since you entered a wallet address, the explorer will show the total balance in the wallet, recent transactions, and the transaction history associated with that address.
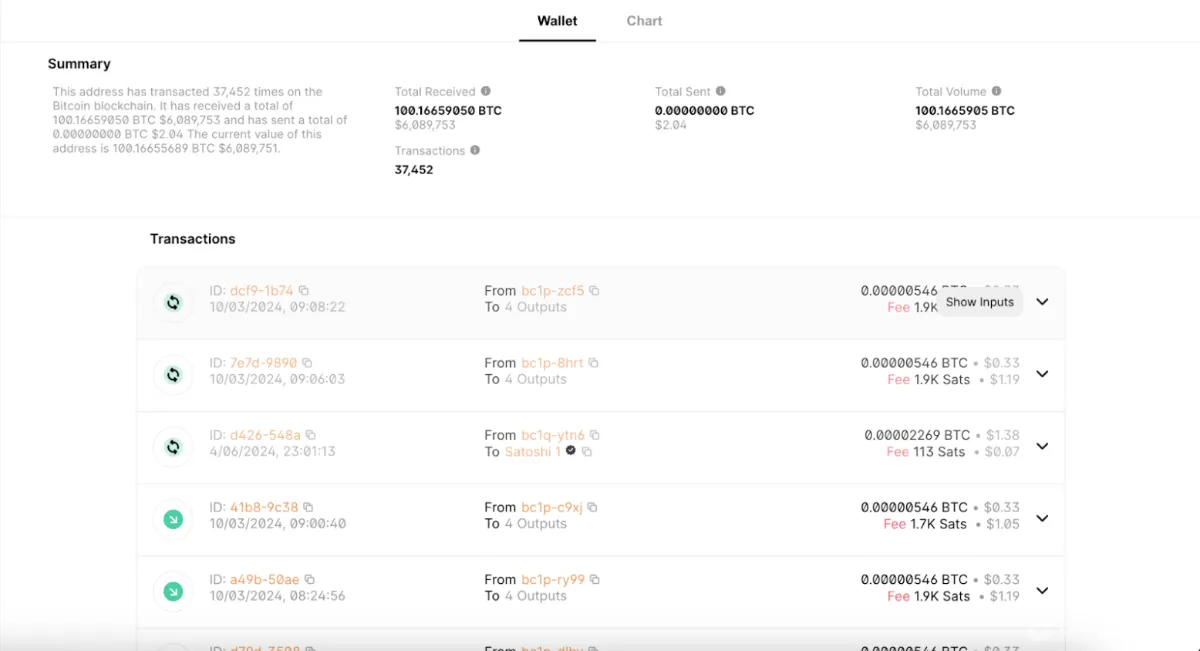
Understanding Key Information on Block Explorers
- Transaction ID: An exclusive identifier for tracking Bitcoin transactions on a block explorer; it reveals details such as the amount, sender, and receiver.
- Addresses: Bitcoin users use public wallet addresses to send and receive funds and change addresses to return excess funds from a transaction.
- Transaction Fees: Miners receive fees for processing transactions, and higher fees lead to faster confirmations.
- Confirmations: Confirmations happen when a miner includes a transaction in a block; many confirmations enhance the transaction’s security and validity.
The Role of Mining in the Bitcoin Public Ledger
Bitcoin mining is important in securing the public ledger and validating transactions. Miners use the Proof of Work (PoW) mechanism to compete in solving complex mathematical problems, with the winner earning the right to create a new block and add it to the blockchain. This process guarantees that transactions are verified and the ledger remains accurate.
Mining rewards, which include block rewards (newly created Bitcoin) and transaction fees from the transactions they confirm, incentivize miners. These rewards encourage miners to continue securing the network. If you’re interested in mining, you can explore Bitcoin mining sites or even learn how to mine Bitcoin at home with the right equipment.
Mining also has important security implications. By requiring significant computational power to solve PoW puzzles, mining protects the network from attacks like double-spending. It guarantees that altering past transactions would require controlling most of the network’s computational power, which is a nearly impossible task, thus keeping the blockchain secure.
Public vs. Private Ledger: Key Differences
Public and private ledgers record transactions but work in different ways:
- A public ledger, like the one used in Bitcoin, is open to anyone. It offers complete transparency, allowing anyone to view and verify transactions.
- A private ledger is restricted to a specific group or organization. Here, access to transaction data is limited to authorized parties.
Knowing the difference is important. It helps to choose the right system for various applications. This depends on the need for transparency, security, and control. In the following list, you will see the main differences between each type of ledger.
Public Ledgers
- Open access for everyone.
- Full transparency of all recorded transactions.
- Decentralized control without a single authority.
Private Ledgers
- Restricted access to authorized people only.
- Limited transparency of transaction data.
- Centralized control by a single entity.
Public ledgers offer several key benefits, particularly transparency, decentralization, and security. Since all transactions are visible and verifiable by anyone, public ledgers promote trust and accountability. Their decentralization means no single entity controls them, making them resistant to censorship, fraud, or tampering. Moreover, using strong cryptographic methods and consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work provides high levels of security, preventing data manipulation.
But public ledgers also have limitations. As transaction volumes grow, scalability becomes an issue — processing can slow down, and the computational power required to maintain the ledger can increase costs. Another limitation is privacy. While your identity remains pseudonymous, the transaction details are fully public, which may not suit situations where confidentiality is critical.
Private ledgers, on the other hand, have their own set of benefits and drawbacks. One of the most significant advantages is privacy. Only authorized parties can access transaction data, making it a better choice for business or sensitive information. These ledgers are also more efficient in processing speed, as there are fewer participants and less computational overhead than public networks. They can also be customized to meet the specific needs of an organization or group. Due to their centralized nature , a single entity or a small group holds control. This can lead to trust issues or vulnerabilities to manipulation. Moreover, restricted access reduces transparency, limiting the ability to conduct external audits or verifications.
Public ledgers are best suited for use cases like cryptocurrencies, where transparency and decentralization are paramount. For instance, Bitcoin and Ethereum rely on public ledgers to create a trusted, decentralized system for peer-to-peer digital payments. They are also used in supply chain management, where many parties need to verify the movement of goods across complex global networks. Decentralized finance (DeFi) applications also use public ledgers to enable financial services like lending, borrowing, and trading without relying on intermediaries.
On the other hand, enterprises often use private ledgers for internal operations, such as managing inventory, employee records, or financial transactions. They are also popular in industries like banking or healthcare, where consortium networks allow for secure collaboration between trusted parties. Governments also use private ledgers to manage sensitive data, such as tax records, citizen identification, or land ownership registries. This guarantees privacy while maintaining control over the information.
Final Thoughts on the Bitcoin Public Ledger
Key features of the Bitcoin public ledger include transparency, security, and decentralization. It allows anyone to view transactions while using cryptographic methods and Proof of Work for security. Its decentralized nature prevents control by any single entity, making it resistant to tampering and censorship, ensuring network integrity.
Public ledgers like Bitcoin’s promote transparency and accountability by allowing anyone to verify transactions without relying on a central authority. Using block explorers can help users understand the system and verify transactions independently.
For those looking to dive deeper, it’s important to understand what Bitcoin mining difficulty is. Mining difficulty secures the network by ensuring that transactions are validated in a fair and balanced manner. Exploring these concepts will improve your knowledge of the inner workings of Bitcoin and its public ledger.
FAQs


















 Ines S. Tavares
Ines S. Tavares 
 Ihssan El Medkouri
Ihssan El Medkouri 
 Anatol Antonovici
Anatol Antonovici